 Book Online
Book Online

Stroke, sometimes called a brain attack, is the most serious medical emergency, and prompt treatment is crucial. Early action can reduce brain damage and prevent further complications. A stroke occurs when the blood supply to a part of your brain is interrupted or severely reduced, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients. Within minutes, brain cells begin to die. It is caused by the blockage of blood flow or the rupture of an artery to or in the brain.
The reasons for a stroke are broadly classified into two categories.
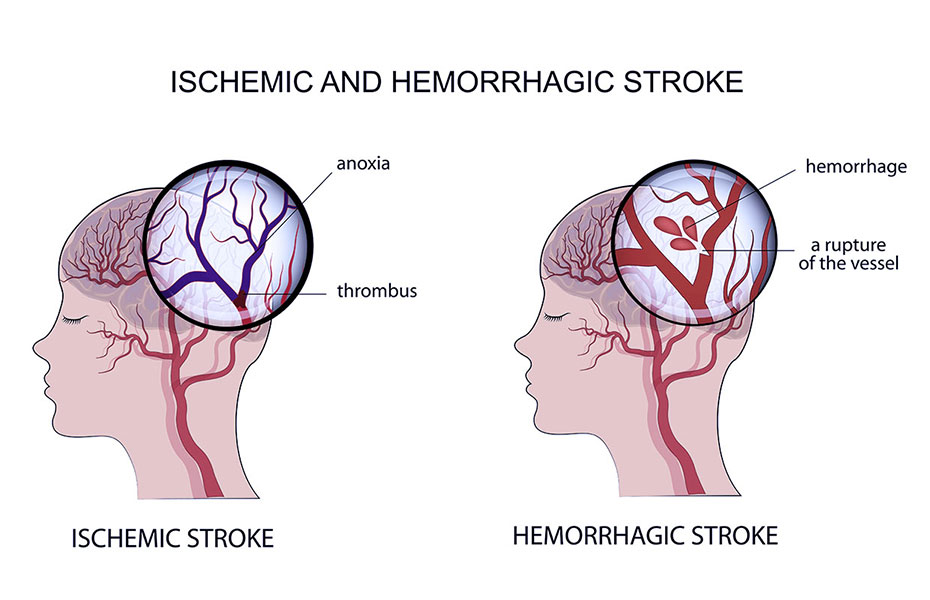
Ischemic stroke are of two types:
Cerebral Embolism: This occurs when a blood clot forms in another part of the body, such as the heart or arteries in the upper chest and neck. The clot then moves through the bloodstream until it reaches an artery too narrow to allow it to pass. The clot becomes lodged, blocking the flow of blood and causing a stroke.
Cerebral thrombosis: This type of ischemic stroke happens when a blood clot develops at the fatty plaque within a blood vessel.
Transient Ishemic Attack (TIA): TIA, often referred to as a mini-stroke, is characterized by the sudden onset of neurological deficits that last for less than 24 hours. It occurs when there is a temporary blockage of blood flow to the brain. TIAs serve as warning signs that a full-blown stroke may occur in the future. It is essential to seek medical attention promptly when experiencing TIA symptoms to assess and manage the underlying risk factors and prevent a potential stroke.
There are two types of Hemorrhage:
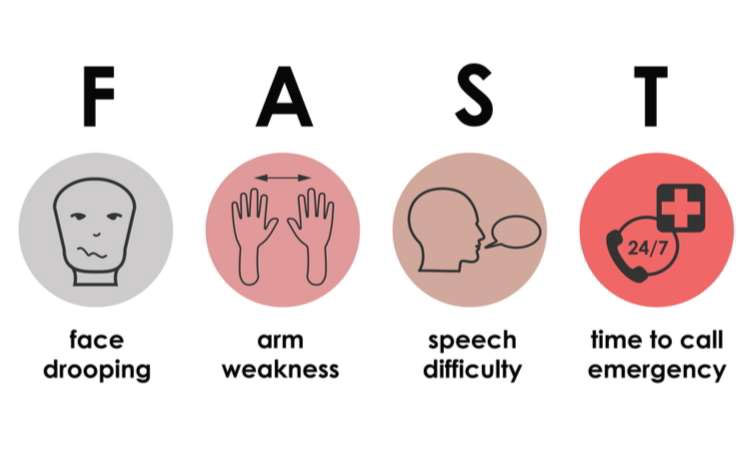
Signs and symptoms of a stroke typically begin suddenly and can vary from person to person.
Common signs and symptoms of a stroke include:
ACTING F.A.S.T IS KEY FOR RECOGNIZING AND RESPONDING TO A STROKE
If you think someone may be having a stroke, remember:
01. Modifiable Risk Factors
02. Non-modifiable Risk Factors
Stroke rehabilitation is enhanced by an integrated and holistic treatment approach that addresses the varied aspects of recovery, including physical, cognitive, emotional, and social dimensions. A comprehensive treatment plan is crafted through collaboration among diverse healthcare professionals, offering tailored care to meet individual needs. Here are the key components of such an integrated and holistic stroke rehabilitation approach:
1. Multidisciplinary Team Collaboration
2. Individualized Assessment
3. Goal Setting with the Individual
4. Physiotherapy
5. Robotic rehabilitation
6. Occupational Therapy
7. Speech-Language Therapy
8. Ayurveda
9. Psychological Support
10. Reflexology
11. Acupuncture
12. Yoga
13. Cognitive Rehabilitation
14. Social Work and Community Integration
15. Nutritional Assessment and Management
16. Medication Management
17. Home Modification and Adaptive Equipment
18. Community Reintegration and Vocational Rehabilitation
19. Holistic Wellness Promotion
20. Caregiver Education and Support:
21. Ongoing Monitoring and Adjustments
The holistic and integrated nature of stroke rehabilitation ensures a comprehensive approach to the individual's recovery, addressing physical, cognitive, emotional, and social aspects. The involvement of a multidisciplinary team and the collaboration of various healthcare professionals contribute to a more personalized and thorough rehabilitation experience.
Physiotherapy plays a pivotal role in managing and rehabilitating individuals who have experienced a stroke. The goal of stroke physiotherapy is to maximize functional independence, improve mobility, and enhance overall quality of life. The specific approach to physiotherapy may vary depending on the individual's condition, the severity of the stroke, and other factors. Here are key aspects of stroke physiotherapy management:
1. Assessment and Evaluation
2. Goal Setting
3. Treatment Techniques
4. Task-Specific Training
5. Assistive Devices and Adaptive Techniques
6. The Rood’s Approach
7. Bobath Approach or Neuro-Developmental Techniques (NDT)
8. Cardiovascular Exercise
9. Hydrotherapy
10. Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy (CIMT)
11. Patient Education
12. Home Exercise Program
13. Progress Monitoring
It's essential to note that stroke physiotherapy is just one component of a multidisciplinary approach to stroke care. Collaborating with other healthcare professionals, including occupational therapists, speech therapists, and physicians, is crucial for comprehensive stroke management. Additionally, the timing of rehabilitation interventions is critical, and early initiation of physiotherapy can contribute to better outcomes.
Occupational therapy (OT) plays a pivotal role in the rehabilitation of individuals who have experienced a stroke. The primary goal of occupational therapy is to assist individuals in regaining independence in activities of daily living (ADLs) and enhancing their overall quality of life. Here are key components of occupational therapy in stroke rehabilitation:
1. Assessment of Functional Abilities
2. Setting Individualized Goals
3. Task-Specific Training
4. Adaptive Techniques and Equipment
5. Upper Extremity Rehabilitation
6. Cognitive Rehabilitation
7. Home Modification and Safety Assessment
8. Community Reintegration
9. Psychosocial Support
10. Educating Caregivers
11. Progress Monitoring and Adjustment
Occupational therapy is typically a key component of the multidisciplinary stroke rehabilitation team, collaborating with physical therapists, speech therapists, and other healthcare professionals. The emphasis on improving daily functioning and quality of life positions occupational therapy as a critical element in the continuum of stroke care.
Speech therapy, also known as speech-language pathology, is a critical component of stroke rehabilitation for individuals who have experienced communication and swallowing difficulties. Given that stroke can impact various aspects of communication and speech, speech therapists play a key role in assessing, diagnosing, and treating these impairments. Here are key components of speech therapy in stroke rehabilitation:
1. Assessment
2. Communication and Speech Exercises
3. Language Rehabilitation
4. Cognitive-Communication Therapy
5. Aphasia Therapy
6. Dysarthria Treatment
7. Swallowing Rehabilitation
8. Communication Device Training
9. Family and Caregiver Education
10. Home Exercise Programs
11. Progress Monitoring
Speech therapy is a vital component of the multidisciplinary stroke rehabilitation team, working collaboratively with occupational therapists, physical therapists, and other healthcare professionals to address the diverse needs of stroke survivors. The early initiation of speech therapy is frequently essential for maximizing recovery and enhancing the overall quality of life for individuals affected by stroke.
Robotic rehabilitation is an innovative approach that utilizes robotic devices to assist individuals in their recovery after a stroke. These devices are designed to offer targeted and repetitive movements, often in a controlled and adaptive manner. Robotic rehabilitation aims to enhance motor recovery, improve functional outcomes, and promote neuroplasticity. Here are key aspects of robotic rehabilitation in the context of stroke:
1. Assessment and Personalization
2. Gait Training
3. Upper Extremity Rehabilitation
4. Biofeedback and Virtual Reality
5. Adaptive Assistance
6. Repetitive and Intensive Training
7. Task-Specific Training
8. Monitoring and Data Collection
9. Early Initiation of Therapy
10. Complementary to Conventional Therapy
11. Home-Based Rehabilitation
Although there is promise in utilizing robotic rehabilitation for stroke recovery, it's crucial to acknowledge that its effectiveness can differ from person to person. Its optimal impact is often realized when seamlessly integrated into a comprehensive rehabilitation plan.
Ayurveda is a comprehensive healthcare system that considers the body, mind, and soul. It defines health as the balance among 'Doshas', 'Agni', 'Dhatus', 'Malas', and the harmony of 'Atma', 'Indriya', and 'Mana'. According to Ayurveda, being healthy means more than just the absence of illness; it is the balance of all these elements.
Ayurveda offers numerous programs to maintain health, such as 'Dina Chariya' (daily routines) and 'Ritu Chariya' (seasonal routines). When it comes to treating diseases, Ayurvedic treatment is divided into two main categories: 'Sodhana' and 'Samana'.
Sodhana (Purification Therapy):
Sodhana therapies, also known as Panchakarma, aim to purify and detoxify the body. They include:
1. Niruha (Kashaya Vasti): Enema with herbal decoctions
2. Vamana:Therapeutic vomiting
3. Virechana: Purgation or induced bowel movements
4. Nasyam: Administration of medication through the nose
5. Rakta Mokshana: Bloodletting
In Ayurveda, maintaining health is a multifaceted approach, and the balance of these elements ensures overall well-being.
Treatments & Indications
Dhanyamladhara
Indications: Pain, swelling, stiffness, weight reduction, numbness
Indications: Stiffness (Sankocham), muscle tightness, to improve circulation, Niramavastha, Vata predominant pain, relaxation, stress, weight gain
Indications: Chronic pain, deep swelling, joint tightness, muscle relaxant, numbness, heaviness, sensory deficit
Indications: Vata-Pitta (VP) conditions, same conditions as Podikizhi, and all conditions needing more Snigdhatwa (unctuousness)
Indications: Same conditions as Elakkizhi
Gothambukizhi
Indications: As per the selected medium and condition
Njavarakizhi
Indications: Brimhana treatment (nourishing therapy), Ksheena (emaciation), Sosha (wasting condition), to improve muscle bulk, rejuvenation (after completion of treatment)
Pizhichil
Indications: Pain, stiffness, spasticity, sensory deficit, to improve muscle power
Kashaya Dhara (Dashamoola, etc.)
Indications: Amavastha (state of indigestion), pain, Vata-Kapha conditions, Tridosha Hara (pacifying all three doshas), numbness, swelling
Dashamoola Ksheeradhara
Indications: Pain, Vata, Pitta, Rakta associated conditions, burning sensation, wasting, weakness
Udwarthana
Indications: Kapha Hara (reducing Kapha), Medohara (reducing fat), for body and limb firmness, Twak Prasadakara (improving skin texture), heaviness, numbness, flaccidity, obesity, Rookshana Karma (drying therapy)
Shirodhara
- With Thaila (oil)
Indications: Sleep disorders, blood pressure, anxiety, psychological problems, stress, insomnia, fear, improving cognitive functions, concentration
- With Takra (buttermilk)
Indications: Drowsiness, psychological conditions, depression, Rookshana (drying therapy), skin conditions
Nasyam
Indications: Reduces stress and anxiety, neck pain, shoulder pain, improves cognitive functions, relieves sinusitis, improves hearing and balance, facial palsy, cervical spondylosis, headaches, migraines
Raktamoksha
Indications: Detoxification, varicose veins, improves circulation, removes deep-seated toxins, Rakta Pitta disorders, reduces pain and inflammation, blood purification, improves skin health
Vamana
Indications: Detoxification, enhanced digestion and metabolism, respiratory support, reduces excess Kapha dosha, improves skin health and chronic skin conditions, enhances immunity, aids weight management, improves cognition
Virechana
Indications: Obesity or overweight issues, digestive tract issues (e.g., increased acidity, GERD, chronic bloating, sluggish digestion), non-healing wounds, ulcers, abscesses, blisters, diseases of the liver and spleen, PCOS and infertility, skin diseases (e.g., psoriasis, urticaria, acne), metabolic diseases (e.g., diabetes, hypertension, high cholesterol), Vatavyadhi (neurological disorders), Pakshaghata
Niruha Vasthi
Indications: Vata or Vata-predominant diseases, diseases in Vata Ashraya Sthana (sites where Vata resides), conditions requiring Sodhana (purification), colon diseases
Sneha Vasthi
Indications: Diseases affecting the whole body or parts of it, or abdominal viscera, obstruction of urine, flatus, stool, and semen, numbness, muscle wasting, decreased strength, worm infestation, abdominal tumor, body heaviness, dysuria, piles, gout, renal stone, and all diseases caused by vitiated Vata dosha
Vaitharana Vasthi
Indications: Amavata (rheumatoid arthritis), Katishoola (lumbago), Gridhasi (sciatica), Klaibya (sexual dysfunction), Vishama Jwara (fever), Anaha (abdominal distension), Shotha (swelling), Shula (pain). It has Vata-Kapha pacifying properties and helps in removing Avarana of Vata by Kapha.
Ksheera Vasthi
Indications: Vatarakta conditions, Asthivaha Sroto Vikara (bone channel disorders), Sukumara (delicate), Ksheena (emaciation due to work), Vatahara (Vata-pacifying), Balavarna Kara (improves strength and complexion)
Leech Therapy (Jalookavacharana)
Indications: Varicose veins, ulcers (oozing wounds), acne, pimples, cellulitis, hematoma, blood clots in muscle or skin, abscesses, psoriasis
This list provides a detailed overview of various Ayurvedic treatments and their indications, highlighting their holistic approach to health and wellness.
Acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine technique, entails the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate energy flow and foster healing. Widely utilized for various conditions, including pain management and stress reduction, acupuncture has garnered attention for its potential benefits in stroke recovery.
Several studies indicate positive outcomes, particularly in motor function, balance, and overall quality of life for stroke patients. Consider the following ways in which acupuncture may contribute to stroke recovery:
Yoga, a holistic mind-body practice encompassing physical postures, breath control, meditation, and ethical principles, is increasingly recognized for its potential benefits in stroke recovery, although ongoing research continues to explore its specific effects. The emerging evidence suggests that yoga holds promise for various advantages in the rehabilitation of stroke survivors. Below are potential ways in which yoga may contribute to the recovery process: